
 Stockton STEM Badge completed
Stockton STEM Badge completed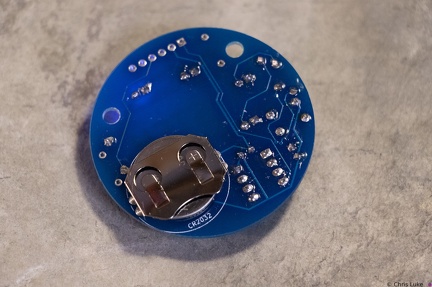 Stockton STEM Badge battery
Stockton STEM Badge battery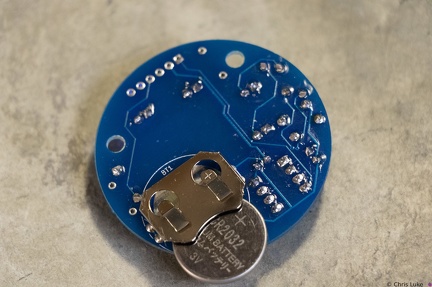 Stockton STEM Badge battery
Stockton STEM Badge battery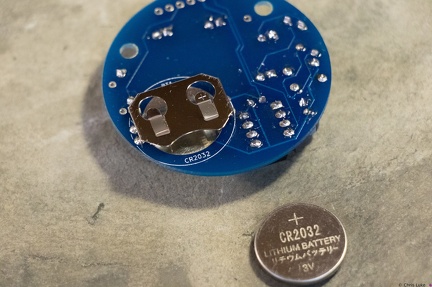 Stockton STEM Badge battery
Stockton STEM Badge battery Stockton STEM Badge IC
Stockton STEM Badge IC Stockton STEM Badge IC
Stockton STEM Badge IC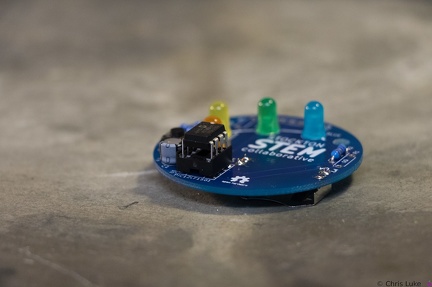 Stockton STEM Badge IC
Stockton STEM Badge IC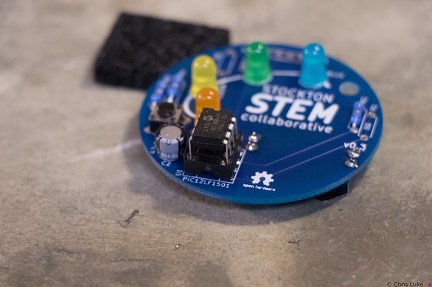 Stockton STEM Badge IC
Stockton STEM Badge IC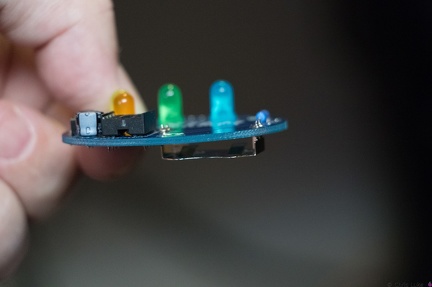 Stockton STEM Badge battery
Stockton STEM Badge battery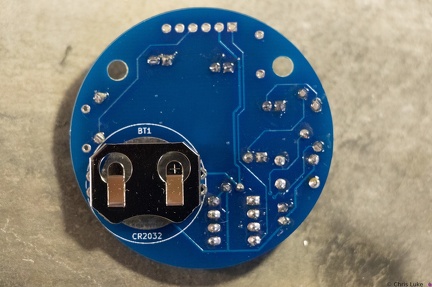 Stockton STEM Badge battery
Stockton STEM Badge battery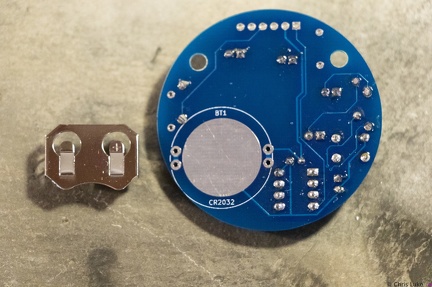 Stockton STEM Badge battery
Stockton STEM Badge battery Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs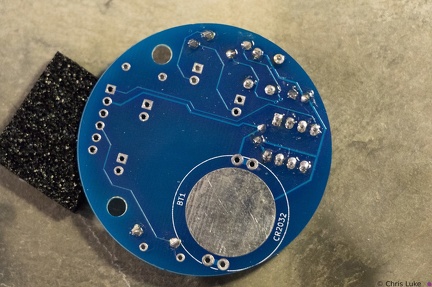 Stockton STEM Badge button
Stockton STEM Badge button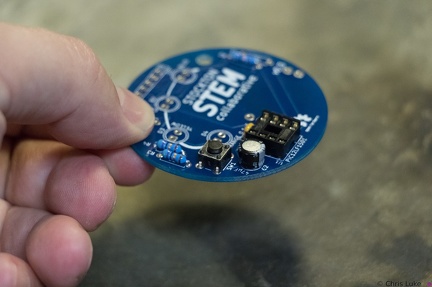 Stockton STEM Badge button
Stockton STEM Badge button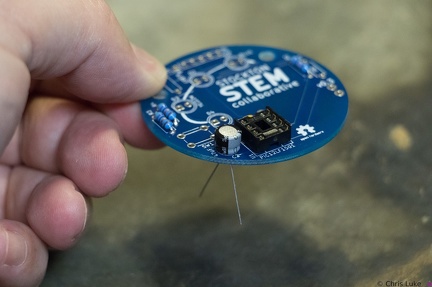 Stockton STEM Badge electrolytic capacitor
Stockton STEM Badge electrolytic capacitor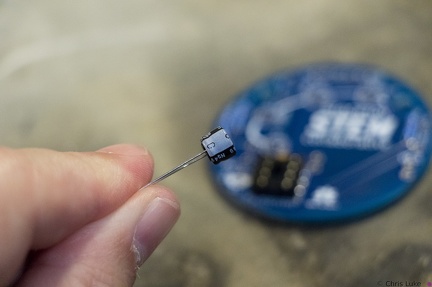 Stockton STEM Badge electrolytic capacitor
Stockton STEM Badge electrolytic capacitor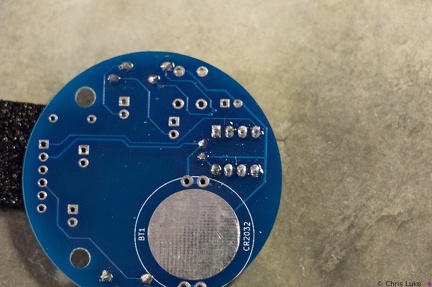 Stockton STEM Badge IC socket
Stockton STEM Badge IC socket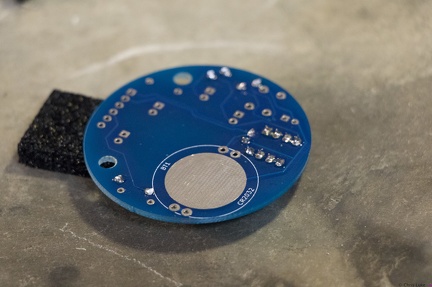 Stockton STEM Badge IC socket
Stockton STEM Badge IC socket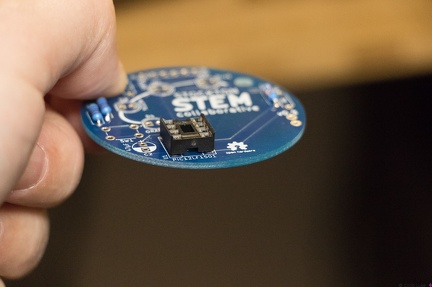 Stockton STEM Badge IC socket
Stockton STEM Badge IC socket Stockton STEM Badge IC socket
Stockton STEM Badge IC socket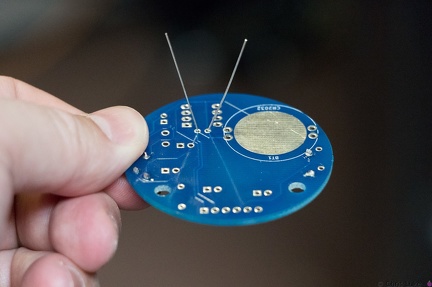 Stockton STEM Badge decoupling capacitor
Stockton STEM Badge decoupling capacitor Stockton STEM Badge decoupling capacitor
Stockton STEM Badge decoupling capacitor Stockton STEM Badge decoupling capacitor
Stockton STEM Badge decoupling capacitor Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs
Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs
Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs
Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs
Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs
Stockton STEM Badge resistor legs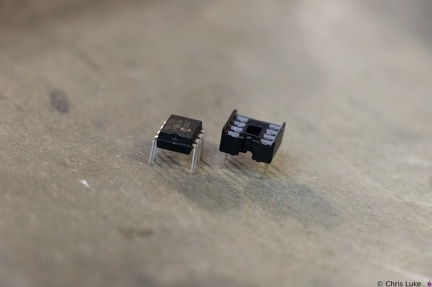 Stockton STEM Badge IC and socket
Stockton STEM Badge IC and socket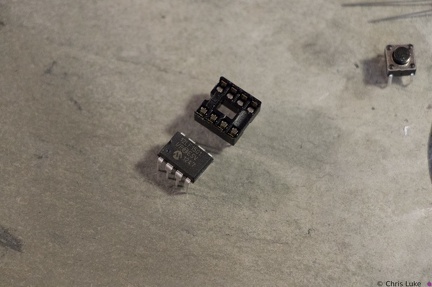 Stockton STEM Badge IC and socket
Stockton STEM Badge IC and socket Stockton STEM Badge components
Stockton STEM Badge components Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs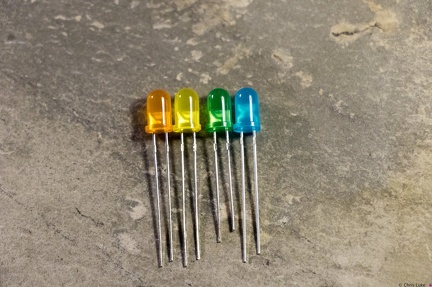 Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs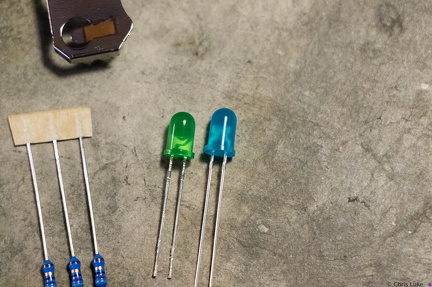 Stockton STEM Badge LEDs
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs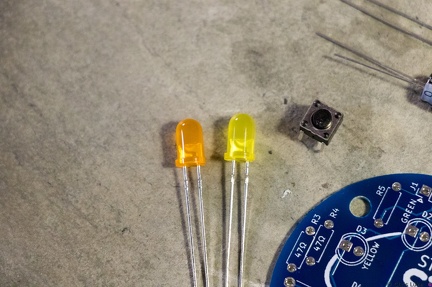 Stockton STEM Badge LEDs and button
Stockton STEM Badge LEDs and button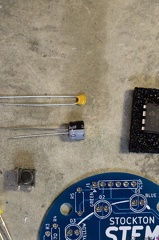 Stockton STEM Badge capacitors
Stockton STEM Badge capacitors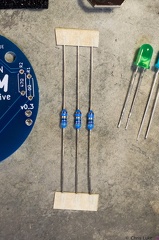 Stockton STEM Badge resistors
Stockton STEM Badge resistors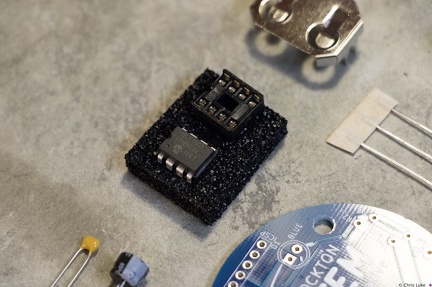 Stockton STEM Badge microcontroller
Stockton STEM Badge microcontroller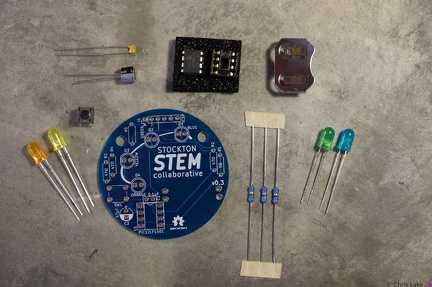 Stockton STEM Badge components
Stockton STEM Badge components Stockton STEM Badge boards
Stockton STEM Badge boards